Summary
Discover how a 20-month international collaboration – featuring Nicoya, Basetwo, CPI, and Labman Automation – is building a first-of-its-kind AI-optimized platform that integrates bioreactor technologies with real-time sensing and control systems. This initiative aims to increase yields, reduce production costs, and improve scalability for next-generation biologics. If you’re in pharma or biotech, this project could redefine how your therapies are made. Read on to learn more.
Inside the BALANCE Project: AI, SPR, and the Next Generation of Bioreactor Automation
How the integration of Alto Digital SPR, AI, and automation is driving a new era of adaptive, efficient biomanufacturing.
Bioreactors are foundational to biologics manufacturing, but ensuring consistent product quality at scale remains a challenge. The BALANCE (Bioreactor Automation for Learning and Adaptive Networked Control of Experiments) project – an international collaborative effort between Nicoya, Basetwo, CPI, and Labman – aims to solve this by integrating AI, automation, and real-time functional biosensing. Read on to learn about how Nicoya’s Alto Digital SPR platform can bring functional quantitation directly into the bioreactor loop, enabling smarter, faster, and more reliable therapeutic production.
Bioreactors: Essential tools for producing therapeutics
Bioreactors are indispensable tools in the world of biopharmaceuticals and industrial biotechnology. They provide a controlled environment for the cultivation of cells which produce key components for various lifesaving medicines and therapeutics, including vaccines, antibiotics and cell therapies. The bioreactors are designed to maintain optimal conditions – temperature, pH, oxygen and nutrient levels – to support cell growth and maximize product yield.
Despite advances in bioreactor design, manufacturers still face challenges related to process consistency, scalability, and product variability. As bioreactors scale up, maintaining uniform conditions becomes more difficult, often resulting in subtle shifts that can impact cell growth and protein expression. For antibody production, even small process deviations can alter glycosylation patterns, affect folding, or lead to the formation of aggregates—all of which affect the safety and efficacy of therapeutics.
The BALANCE project
Recognizing the need for tighter control and functional insight throughout biomanufacturing, a new initiative is bringing together innovators from both sides of the Atlantic. The BALANCE project is a collaborative effort between Nicoya and three other companies, Basetwo, CPI, and Labman, to deliver an AI-optimized demonstrator platform integrating bioreactor technologies with real-time sensing and control systems. Funded by a $2 million joint grant from Innovate UK and the National Research Council of Canada Industrial Research Assistance Program (NRC IRAP), BALANCE aims to bring together the latest in AI, automation, and real-time process control to streamline bioprocessing, ensuring higher yields, lower costs, and improved scalability for next-generation therapeutics. This aims to enhance the precision and efficiency of biologic drug production, offering a smarter, faster path to market.
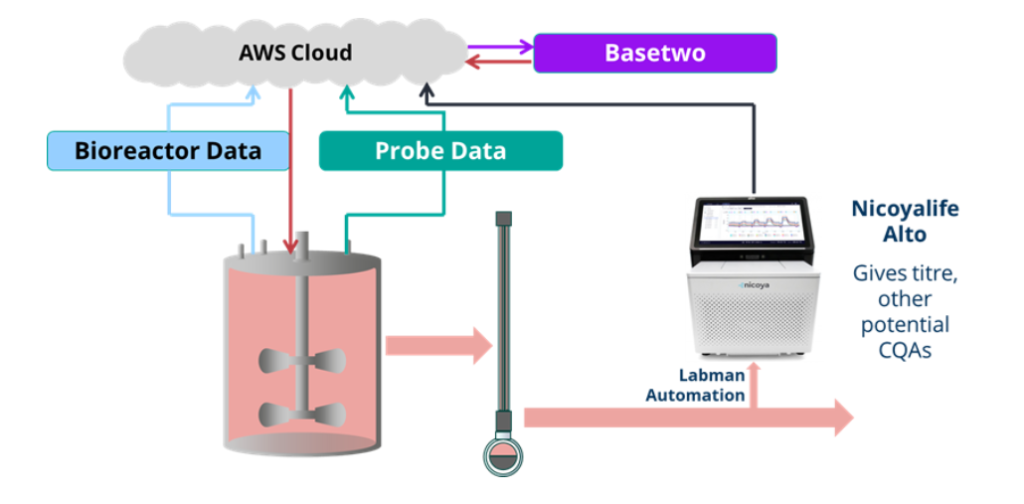
Schematic of the integrated system under development in the BALANCE project. Basetwo’s AI platform will integrate real-time data from both the bioreactor and Nicoya’s Alto Digital SPR to dynamically optimize bioprocess conditions. Labman will design the automation technology that connects all components into a unified system, while CPI will contribute its bioprocessing expertise and bioreactor infrastructure to validate the platform in realistic manufacturing scenarios.
As part of the BALANCE project, Nicoya is contributing its expertise in label-free biosensing through the integration of the Alto Digital SPR platform. Alto will serve as the system’s molecular readout, providing real-time quantification of biomolecules, such as antibodies, directly from crude bioreactor samples. This functional insight is critical for adaptive process control, allowing the AI system to make informed adjustments based not just on environmental parameters, but on actual product performance. Alto’s compact design, crude sample compatibility, and API-based integration make it ideally suited for automated environments, enabling seamless data flow between the bioreactor, biosensor, and AI platform. By embedding SPR-based analytics into live bioprocessing, Nicoya is helping to bridge the gap between production and product quality in real time.
Antibody quantitation by Alto Digital SPR
The Alto Digital SPR platform is the first plate-based SPR system, designed to allow functional biomolecular analysis at every stage of therapeutic development. Alto uses disposable cartridges powered by digital microfluidics (DMF), enabling fully automated, miniaturized assays that reduce hands-on time, sample consumption, and risk of error. Unlike traditional SPR systems that rely on complex tubing and pump-based fluidics, Alto’s tube-free design is inherently resistant to biofouling, allowing direct analysis of the cell culture supernatants in real time without purification. Alto is also built with integration in mind: its API compatibility and compact footprint make it well-suited for automated environments, while its software features support 21 CFR Part 11 compliance, audit trails, and other requirements critical to GxP workflows. From early discovery to regulated manufacturing, Alto delivers actionable, functional, and reliable data.
At the core of Alto’s utility in biomanufacturing is its quantitation module, which enables precise determination of biomolecule concentration. Unlike other common quantitation methods, Alto provides real-time data on crude, unlabeled molecules, while also providing insights into their binding activity, which is essential to their therapeutic effect. The quantitation assay first measures the binding response of biomolecules at a known concentration to generate a logistic calibration curve. Sample is then taken from the bioreactors and measured on the same surface. The binding signal generated by this sample is then placed on the calibration curve to precisely and accurately determine its concentration. As part of the BALANCE project, bioreactor samples will be automatically taken and quantified on Alto at set time intervals, providing continuous information on production efficiency, which will feed back into AI models to optimize the bioreactors’ output in real time.
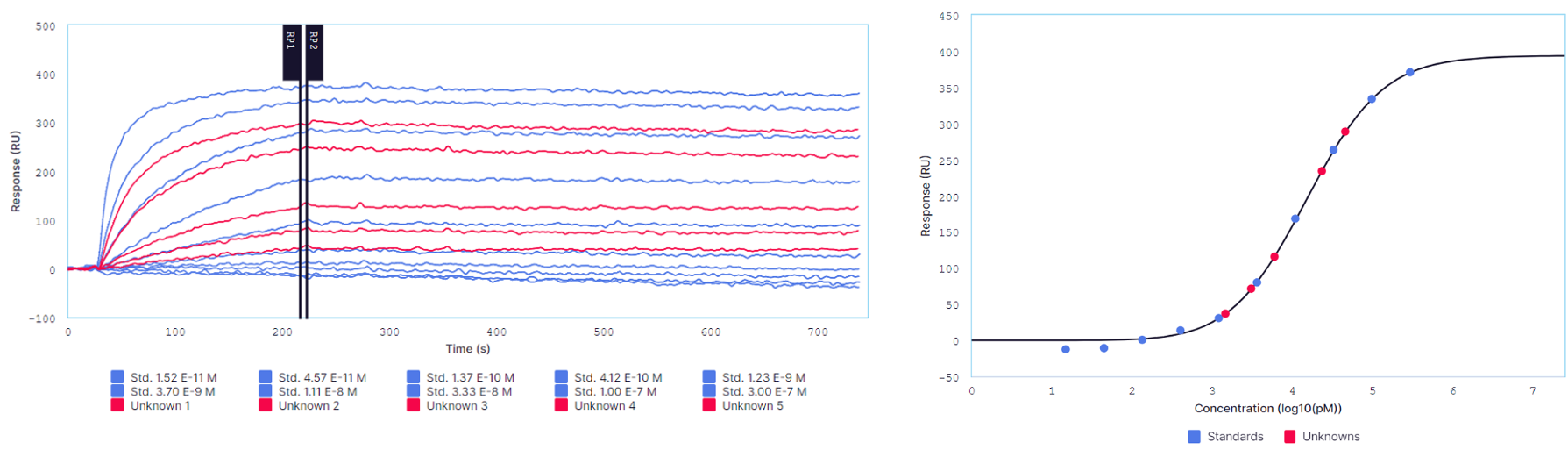
Images taken from Alto’s Nicosystem analysis software showing data from an experiment quantifying antibodies in serum. Antigen was used as the ligand. Binding curves for antibody standards (blue) and unknown samples (red) are shown on the right. The Nicosystem automatically generates a standard curve (left) based on the response of the standards at the user defined report points that is used to determine the concentration of the samples where the antibody concentration is unknown.
Looking forward
As therapeutic manufacturing becomes more sophisticated, so too must the tools that monitor and control it. The integration of functional readouts like those enabled by Alto Digital SPR into bioreactor systems represents a significant leap forward. By moving beyond basic yield measurements to real-time assessments of product activity and quality, manufacturers can unlock new levels of productivity and reproducibility.
At Nicoya, we’re driven by a mission to improve human life by helping life-saving therapies get into patients’ hands sooner. Through our participation in the BALANCE project, we’re pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in biomanufacturing – and delivering the tools manufacturers need to bring safer, more effective therapies to patients, faster.
